Advertisement
Smart assistants have mostly lived inside phones and speakers, answering questions and setting timers. The Rabbit R1 changes that. This bright-orange device isn’t just another screen—it wants to be your digital companion in a more direct way. Rather than having you open apps or navigate menus, it’s designed to take action for you. The Rabbit R1 is an AI device designed to simplify everyday tasks, not by providing you with more options but by handling things on your behalf. It doesn't pretend to be a supercomputer, but it aims to make interaction feel personal again.
The Rabbit R1 uses a voice interface, a rotating camera, and a large button for input. At its core is something called the Large Action Model (LAM). Unlike language-based models that generate responses, this one is trained to understand how people use apps and websites—like booking a ride, ordering food, or adjusting smart devices.
When you give a command, it doesn’t just suggest something. It imitates how a person would navigate an app to complete a task. You might say, "Order lunch from the place where I got food last Tuesday," and the Rabbit R1 handles the process from start to finish.
This approach sets it apart from other AI tools. Those are good at offering information or suggestions. The Rabbit R1 tries to do the task itself. It behaves more like a remote worker than a search engine. Its goal is to replace time-consuming digital steps with a few words.
The Rabbit R1 looks different from most devices. It’s a small, square gadget about the size of a deck of cards. It has a 2.88-inch screen, a scroll wheel, a rotating camera, and a talk button. The scroll wheel isn’t decorative—it helps you go through previous interactions and messages. The rotating camera isn’t for selfies—it’s meant to scan objects and understand the physical environment.
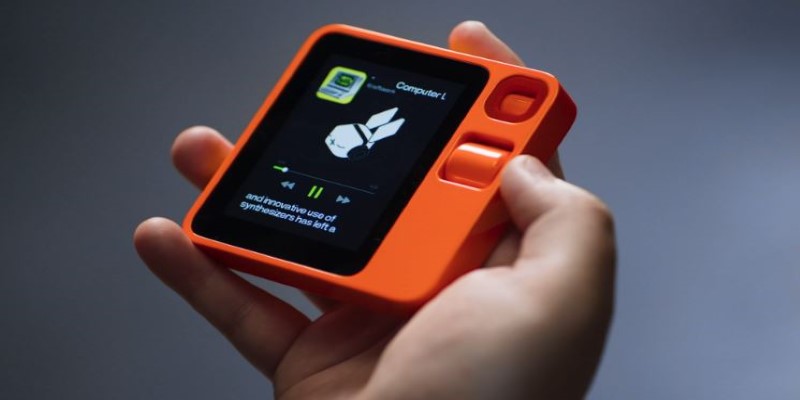

This device isn’t meant to be a desk ornament. It fits in a pocket, is tactile, and invites short, purposeful use. The talk button feels more like a walkie-talkie, encouraging quick commands rather than long conversations.
When in use, the Rabbit R1 shows its activity on-screen in real time. You can see it navigating apps, selecting options, and completing steps. That adds a layer of transparency. You’re not left wondering if it understood your request—it shows you what it’s doing.
It does require internet access—Wi-Fi or mobile data—to function well. But when connected, it responds quickly and consistently, making it practical for everyday tasks.
Most AI today either lives inside apps or runs on the cloud. The Rabbit R1 is different. It’s a standalone AI device meant to operate independently. It’s not a feature inside something else—it’s the main event.
Its Large Action Model isn't focused on generating responses. Instead, it's built to operate apps the way people do. It watches how humans navigate software and then repeats those steps. That means it can work across different platforms without needing custom integrations or plugins.
This makes it potentially more flexible than AI assistants tied to specific ecosystems. Other tools often rely on partnerships or API access to function. The Rabbit R1 doesn't. It utilizes both visual and procedural learning to perform tasks like a human.
This isn’t without complications. Apps and websites change constantly. Teaching AI to keep up without breaking is tough. There are also privacy concerns when a device logs into services and acts for you. Rabbit says it handles most tasks locally and uses authentication systems to give users control, but it's still a new space.
Even with those challenges, the device shows what a hands-on AI assistant might look like. It doesn’t aim to impress with knowledge—it aims to take action, which is what many users want.
Plenty of devices try to be helpful, but most feel like tools. The Rabbit R1 tries to feel like a simple, responsive assistant. It doesn’t mimic emotions or try to sound human. It just works.
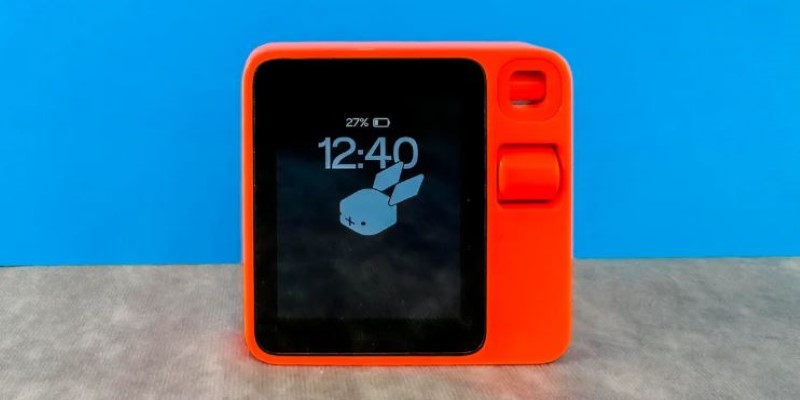

Its camera isn't for photos—it's for object recognition. You can show it something, like a receipt or product, and it will figure out what to do next. That makes it useful in ways that go beyond voice. It also becomes a visual assistant.
Combined with the scroll wheel and voice button, it offers a different kind of interface. You don’t tap through menus or type things out. You press a button, speak, and it responds with actions.
Its real value is focus. It’s not trying to replace your phone or become another screen in your life. It’s built to handle a handful of things well: listening, understanding, and doing. That’s rare in a world of devices that try to be everything.
For people frustrated by juggling apps or wasting time on routine tasks, this kind of tool is refreshing. It doesn't offer distractions. It offers help, saving effort and clicks and making everyday tasks feel less exhausting.
The Rabbit R1 is still early in its development, and it will need updates and feedback to grow. But it’s doing something different—it’s acting instead of just informing. It doesn’t want to be another smart device that gives you choices. It wants to take care of tasks that slow you down or distract you from your day. And that makes it stand out more than most. The Rabbit R1 may not be perfect, but it suggests a future where AI doesn't just talk—it acts with real, useful intent. That shift could be exactly what users need in a time when attention and time are constantly pulled in too many directions.
Advertisement

How LLM evaluation is evolving through the 3C3H approach and the AraGen benchmark. Discover why cultural context and deeper reasoning now matter more than ever in assessing AI language models

How to run LLM inference on edge using React Native. This hands-on guide explains how to build mobile apps with on-device language models, all without needing cloud access

Language modeling helps computers understand and learn human language. It is used in text generation and machine translation

Discover the Playoff Method Prompt Technique and five powerful ChatGPT prompts to boost productivity and creativity

How One Hot Encoding converts text-based categories into numerical data for machine learning. Understand its role, benefits, and how it handles categorical variables

Explore the Rabbit R1, a groundbreaking AI device that simplifies daily tasks by acting on your behalf. Learn how this AI assistant device changes how we interact with technology

Natural language generation is a type of AI which helps the computer turn data, patterns, or facts into written or spoken words
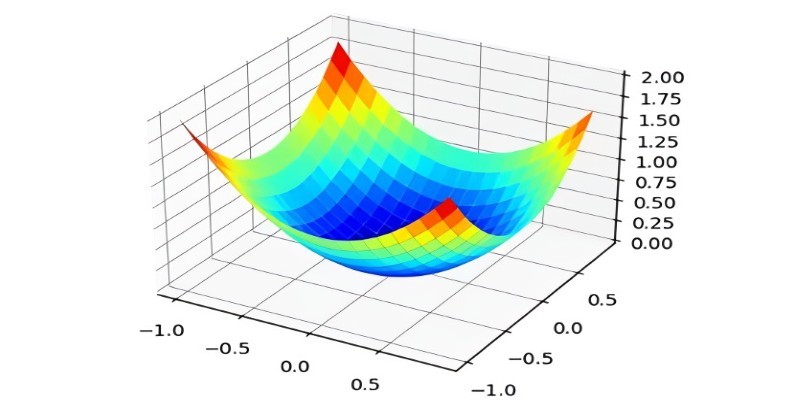
What the Adam optimizer is, how it works, and why it’s the preferred adaptive learning rate optimizer in deep learning. Get a clear breakdown of its mechanics and use cases
How temporal graphs in data science reveal patterns across time. This guide explains how to model, store, and analyze time-based relationships using temporal graphs

Looking for the best podcasts about generative AI? Here are ten shows that explain the tech, explore real-world uses, and keep you informed—whether you're a beginner or deep in the field

How AI-powered earthquake forecasting is improving response times and enhancing seismic preparedness. Learn how machine learning is transforming earthquake prediction technology across the globe

How Krutrim became India’s first billion dollar AI startup by building AI tools that speak Indian languages. Learn how its large language model is reshaping access and inclusion